 “Local electrical characterization of cadmium telluride solar cells using low-energy electron beam”, H. P. Yoon, P. M. Haney, D. Ruzmetov, H. Xu, B. H. Hamadani, A. A. Talin, and N. B. Zhitenev, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 117, 499-504, 2013.
“Local electrical characterization of cadmium telluride solar cells using low-energy electron beam”, H. P. Yoon, P. M. Haney, D. Ruzmetov, H. Xu, B. H. Hamadani, A. A. Talin, and N. B. Zhitenev, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 117, 499-504, 2013.
1. Center for Nanoscale Science and Technology, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD 20899.
2. Energy and Environment Division, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, Maryland, 20899, USA.
3. Maryland Nanocenter, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA
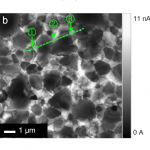
ABSTRACT. We investigate local electronic properties of cadmium telluride solar cells using electron beam induced current (EBIC) measurements with patterned contacts. EBIC measurements are performed with a spatial resolution as high as ≈20 nm both on the top surface and throughout the cross-section of the device, revealing an enhanced carrier collection in the vicinity of grain boundaries. Furthermore, we measure local current-voltage characteristics using contacts with dimension both larger (≈5 µm × 10 µm) and smaller (≈1 µm × 1 µm) than the device thickness (≈4 µm), finding that the value of local open-circuit voltage is also larger near grain boundaries.

